Mid-season cabbage varieties obtained in the 70–80s of the last century are popular due to their versatility and other advantages. The grade SB-3 F1 is different in that it is suitable for cultivation in any climatic zones. About its features and agricultural cultivation technology - further in the article.
Selection History SB-3 F1
The grade SB-3 F1 was obtained back in 1984 at the Moscow Breeding Station. Timiryazev. Experimenting with different varieties, breeders tried to get a variety with high yields, friendly ripening and the possibility of growing in any climatic zones without a significant reduction in yield. Officially, the new variety was registered in the State Register in 1990.
Did you know? At least 100 different types of cabbage are grown all over the world, but the most common are white, red and cabbage.
Description and characteristic
White cabbage SB-3 F1 is a representative of the cruciferous family. She is a biennial. In the first year of growth, a stem forms on which the head of the cabbage forms, and in the second year, a peduncle appears on which the seeds ripen. SB-3 F1 is suitable for cultivation in any region - this is one of the main features of the variety.
Excellent appearance and commercial qualities make it suitable for growing on a large industrial scale. The variety is considered universal and is appreciated in cooking. It is perfectly stored, can be used fresh and is suitable for all types of workpieces. Cabbage gained high palatability due to its high sugar content. Her taste is rated at 4.5 points out of 5 possible.
Main characteristics of cabbage SB-3 F1:
- leaf rosette: large, raised, with a diameter of up to 90 cm, a height of up to 60 cm;
- head: rounded, dense, light green;
- leaves: medium sized, rounded, with a small number of veins, pale green with a dark gray additional shade, waxing is absent;
- weight: 3-4,4 kg;
- diameter: medium - 17-24 cm;
- texture: dense, crispy;
- stump: small, short;
- taste: sweetish;
- tolerance / stability: the variety is resistant to black leg, formosis;
- ripening period: 130–140 days;
- palatability: high;
- productivity: 970–1018 kg / ha.
It can be grown in seedling and seedling methods. The variety is characterized by excellent keeping quality and the possibility of long storage fresh.
Did you know? A few years ago a monument appeared in Kiev called “You Will Have a Child”. The monument is a bronze cabbage, on top of which lies a baby. As conceived by the authors, the monument should help couples who came to him to give birth to a healthy child.
Appearance of cabbage
Traditional cabbage varieties are increasingly being replaced by new hybrid varieties. SB-3 F1 is also a first-generation hybrid variety. Hybrids are more productive and resistant to fungal and viral diseases. In appearance, they do not differ from ordinary varieties: there is a leaf rosette with a cabbage head on the leg.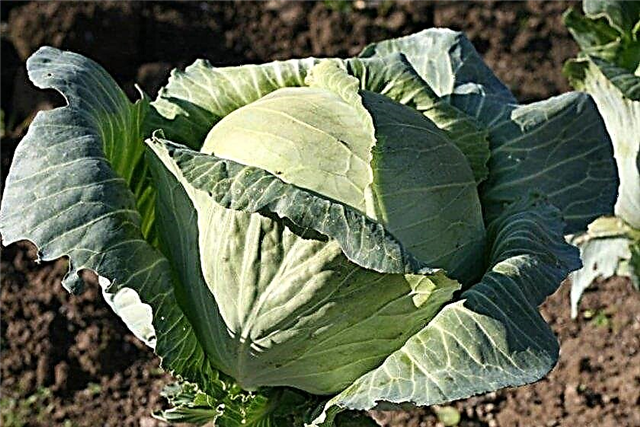
Ripening dates and productivity
The described variety can be grown using seedlings or planted directly on an open bed. Planting dates will affect the timing of the harvest. For cabbage with a ripening period of 130–140 days, it will be better to plan the planting in seedlings. To do this, the seeds are planted in cups 3-4 weeks before planting in the ground.
The optimal time for sowing seedlings is from April 10. Then seedlings are planted on the garden at the end of May. The yield declared by the originator is one of the highest: 970–1018 c / ha. The description of this variety in the State Register indicates that the maximum yield was 1260 kg / ha. This indicator is usually affected by watering and fertility of the site.
Resistance to cold and disease
The variety can grow in any climatic conditions, including in Siberia, so when planning a planting, consider not frost resistance, but the duration of the growing season. So, in regions with a short summer, varieties that require more than 4 months to develop, it is advisable to grow in greenhouses. SB-3 F1 cabbage tolerates drought and other adverse weather conditions. Of the diseases, the resistance of the variety to the black leg and formosis was noted. Heads are resistant to cracking.
Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
- Advantages of grade SB-3 F1:
- very high productivity;
- excellent taste;
- good adaptation to all types of climate;
- frost resistance;
- drought tolerance;
- good keeping quality;
- excellent presentation of heads of cabbage, which does not deteriorate during transportation;
- friendly ripening;
- resistance to cracking.
- Among the shortcomings are noted:
- long ripening period, despite the fact that the variety is indicated as mid-season;
- insufficient protection against diseases, but this is inherent in all varieties of the old selection.
The rules for growing varieties
To obtain a high yield and high-quality marketable fruits, you need to grow good seedlings, and then provide the plants with optimal conditions for growth and development. However, you will need to carefully prepare the site for growing cabbage. Preplant planting involves the preparation of seeds, soil, containers for growing.
Important! For more northern regions, the date of planting cabbage seeds in open soil is shifted by 1–2 weeks and falls on the beginning of May.
Seedlings begin to be prepared in April to plant plants in the ground in May. The period of growing seedlings is 30–35 days. During this time, 3-5 real leaves should form on the plants. The optimal time for planting seeds in unprotected soil without preliminary seedling cultivation is April 20–25. This method is only suitable for southern regions with a warm climate. Seedling method allows you to accelerate the harvest
Seedling method allows you to accelerate the harvest
Preparing seeds for sowing
Basic actions with seeds:
- calibration
- disinfection;
- germination.
Calibration is the process of selecting large germinating seeds. To do this, they are soaked in a solution of ordinary salt (3%) for 5 minutes. Empty seeds will pop up - they can be thrown away because they will not germinate. The remaining seeds can be planted all or choose larger ones. This greatly affects the size of future plants. The larger the seed, the higher its potential for development. To protect the future crop from pathogenic microorganisms, the seeds are disinfected in hot water (+ 50 ° C). The same effect is achieved by soaking in a weakly pink solution of potassium permanganate for 20-30 minutes. For germination, the seeds are laid on a saucer and covered with a damp cloth. The temperature in the room should be normal - about + 20 ° C. After 3 days, the seeds should hatch. If less than half has sprouted - wait a couple more days and you can plant them in the ground.
To protect the future crop from pathogenic microorganisms, the seeds are disinfected in hot water (+ 50 ° C). The same effect is achieved by soaking in a weakly pink solution of potassium permanganate for 20-30 minutes. For germination, the seeds are laid on a saucer and covered with a damp cloth. The temperature in the room should be normal - about + 20 ° C. After 3 days, the seeds should hatch. If less than half has sprouted - wait a couple more days and you can plant them in the ground. After soaking, the ponytails hatch from the seeds. To plant the seeds, prepare the container. It can be wooden boxes, plastic or paper cups. The best containers are peat cups and peat tablets. A peat cup for growing seedlings is filled with soil mixture, after which cabbage is planted on the garden bed without being removed from the container.
After soaking, the ponytails hatch from the seeds. To plant the seeds, prepare the container. It can be wooden boxes, plastic or paper cups. The best containers are peat cups and peat tablets. A peat cup for growing seedlings is filled with soil mixture, after which cabbage is planted on the garden bed without being removed from the container.
Did you know? The Roman emperor Diocletian is known not only for renouncing power in order to grow cabbage in his estate, but also for the fact that he has developed several new varieties that he was very proud of.
In addition, peat is an additional fertilizer. Peat tablets are peat packed in a net. It is moistened, a seed is planted and placed in a container for germination. Such seedlings immediately grow in a nutrient medium, and when planted, they do not undergo deformation, as they plant together with the medium in which they grew.
Video: sowing cabbage seeds for seedlings
Further seedling care
After sowing the seeds, the temperature for them is set at +18 ... + 20 ° C. Seedling sprouts will appear on the 4th – 5th day after planting. After that, the temperature is reduced to +7 ... + 9 ° C. Be sure to monitor the condition of the soil so that it does not dry out. It is advisable to grow seedlings with additional illumination. Under normal lighting, seedlings will stretch toward the light source. To make them grow even, containers with seedlings must be illuminated with fluorescent or LED lamps. Feeding is carried out when 2 leaves are formed on each plant. The composition of the dressing: 1 tbsp. l urea, 1 tbsp. potassium sulfate, diluted in 10 liters of warm water. Top dressing is introduced in the form of basal fertilizer. The second top dressing can be applied directly a few days before transplanting seedlings into the ground. Plants that are grown in peat tablets can not be fed. Before planting in a permanent place, all plants must be abundantly watered.
Feeding is carried out when 2 leaves are formed on each plant. The composition of the dressing: 1 tbsp. l urea, 1 tbsp. potassium sulfate, diluted in 10 liters of warm water. Top dressing is introduced in the form of basal fertilizer. The second top dressing can be applied directly a few days before transplanting seedlings into the ground. Plants that are grown in peat tablets can not be fed. Before planting in a permanent place, all plants must be abundantly watered.
Did you know? Folk legends of Russia explained the appearance of children in cabbage by the fact that a hare brings them there — symbol of fertility. And he chose cabbage because its wide leaves are like diapers.
Site and ground preparation
Site preparation begins in the fall. You need to choose a site on which legumes or root crops grew before cabbage. You can not plant the same plants in the same area for several years, since pests and pathogens accumulate in the soil, which can infect plants and reduce productivity. The site should be well-lit and well-drained. Cabbage can grow on any soil, but loam is considered preferred.
Autumn digging of the soil is combined with the removal of weeds, pest control and lime for deoxidation if the acidity level is above 6–6.5 pH. If the plants in the selected area were sick with fungal diseases, then the soil is disinfected with a hot solution of copper sulfate (1 tbsp. Per 10 liters of water). Some gardeners bring humus or manure to the plot in the fall. But along with melting snow, the nutrients of such fertilizers will go to deeper layers of the soil, from where cabbage cannot get them, therefore it is advisable to introduce humus in the spring at the rate of 5-8 kg / 1 m². If you apply fertilizers of inorganic origin, then these can be:
Some gardeners bring humus or manure to the plot in the fall. But along with melting snow, the nutrients of such fertilizers will go to deeper layers of the soil, from where cabbage cannot get them, therefore it is advisable to introduce humus in the spring at the rate of 5-8 kg / 1 m². If you apply fertilizers of inorganic origin, then these can be:
- urea - 1 tbsp. l .;
- superphosphate - 1 tbsp. l .;
- wood ash - 1 tbsp.
Did you know? In the national sowing calendar, the recommended date for planting seedlings — May 18th. This is the day of Irina the hotbed.
Transplanting seedlings in the open ground
When the time comes to plant seedlings in the ground, it should be quite strong:
- approximate stem height - about 15 cm;
- the number of true leaves is 3-5.
Plan a transplant on a dry day at an outdoor temperature of at least + 10 ° C. In terms of planting in open ground - this is the last decade of May. If seedlings were grown in plastic containers, then planting is carried out by the method of transshipment. Plants that grew in peat pots or tablets are planted with the container. To make the process of planting in the ground painless, seedlings are stopped watering a few days before the intended planting date. And 1-1.5 hours before disembarkation, it is shed with water so that the earthen lump becomes not just wet, but wet. Then it will not decay during transplantation, and the plants will not suffer much. The holes are prepared a little larger than the root system of seedlings. Planting depth - to the bottom leaves. It is necessary that the distance between individual plants is at least 40 cm. The distance between rows is 50–55 cm. Seedlings are certainly planted in the absence of sun.
To make the process of planting in the ground painless, seedlings are stopped watering a few days before the intended planting date. And 1-1.5 hours before disembarkation, it is shed with water so that the earthen lump becomes not just wet, but wet. Then it will not decay during transplantation, and the plants will not suffer much. The holes are prepared a little larger than the root system of seedlings. Planting depth - to the bottom leaves. It is necessary that the distance between individual plants is at least 40 cm. The distance between rows is 50–55 cm. Seedlings are certainly planted in the absence of sun.
Basic rules for the care of cabbage
Cabbage grows easily and provides a crop rich in nutrients. But for this you must provide the plants with proper care. This contributes to the good development of plants and a rich harvest. After planting, cabbage will need:
- regular watering;
- periodic top dressing;
- loosening;
- hilling;
- pest control measures.
Important! A glass of raw cabbage juice, drunk 1 time per day, will relieve you of migraines for a long time.
Intensity of watering and top dressing
White cabbage requires regular watering. If seedlings are only planted in the ground, then they are watered 3-4 times a week. The volume of water is up to 2 liters per plant. After a month, watering is reduced to 1 time per week. The volume of water is 10-12 l / 1 m².
As for watering methods, there are several:
- along the furrows but in this case it is difficult to control the uniformity of irrigation;
- by sprinkling (using sprinklers) - while water falls on the leaves, which contributes to the development of fungal infections;
- drip irrigation - it is the most rational, because it allows you to economically consume water and feed it directly under the roots.

You need to feed cabbage 3-4 times per season. The best fertilizer option is a balanced composition of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in a ratio of 10:10:10.Complex fertilizers are used for top dressing or you can create top dressings from several types at once:
- Ammonium nitrate (10 g / 10 l of water) - The best inorganic source of nitrogen. Its composition is about 40%. Nitrogen is needed in order for the intensive development of the leaf part of the plant to occur. Norm - 40–45 g / 1 m².
- Superphosphate - a source of phosphorus, which is needed for the development of the root system and flowering. The norm of its application is 40 g / 1 m².
- Potassium chloride - a source of potassium, which is needed to activate metabolic processes in plant cells. The application rate is 30–40 g / 1 m².
Video: feeding cabbage
Loosening and weeding
Loosening is necessary for the plant in order to weaken the soil and provide an opportunity for the development of roots. Carry it out a day after irrigation or rainfall. Combine with weed removal. The recommended depth of cultivation is 7 cm. Cabbage is often planted using spunbond or agrofibre as a mulch. The bed is covered with a film, cuts are made in it and cabbage is planted in them. This method of garden design prevents the growth of weeds, reduces the number of soil pests due to intensive heating of the soil, prevents new pests from entering the soil, and also helps to retain moisture after irrigation.
Cabbage is often planted using spunbond or agrofibre as a mulch. The bed is covered with a film, cuts are made in it and cabbage is planted in them. This method of garden design prevents the growth of weeds, reduces the number of soil pests due to intensive heating of the soil, prevents new pests from entering the soil, and also helps to retain moisture after irrigation.
Pest and Disease Control
If you grow cabbage correctly, observing the requirements for the plot, microclimate, frequency of watering and fertilizing, then you can count on the successful harvest, not damaged by diseases and pests. If the weather is unfavorable, then various diseases can manifest themselves. Diseases are fungal, bacterial or viral in nature.
The main fungal diseases:
- Kila - a dangerous disease that affects the root system. Instead of roots, cabbage forms growths that do not conduct water and nutrients from the soil to the leaves. The roots themselves die. As a result, the plant dies. The spores of the fungus spread with wind, moisture, insects and tools that process the soil. The disease is not treated, therefore, if infected plants appear on your site, they must be destroyed, and the site should not be used for planting cabbage for at least 5 years. The next season, a variety resistant to keel is planted, but on a different site.
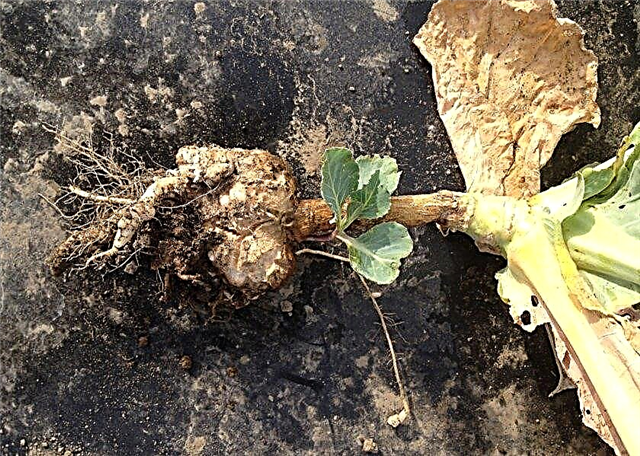

- Peronosporosis, or downy mildew - manifests itself in the form of a flour-like coating on the leaves and yellowish spots. For treatment, a solution of Bordeaux fluid (1%) is used.

- Fusarium - due to blockage of blood vessels in the leaf tissue, the leaves turn yellow, and then die. A head of such a plant hardly develops. As a prophylaxis, crops are treated with copper-based fungicides or with Topsin-M and Benomil preparations.

The main viral disease of cabbage is a mosaic. It appears as black dots on the surface of the leaves. The mosaic virus is often carried by insects: aphids, ticks, so treatment should include the destruction of pests.The disease itself is considered incurable. The affected plants are dug up and destroyed. Diseases of a bacterial nature also cannot be treated. Such plants are dug up and burned away from the site.
Significant harm to cabbage is caused by insects. Some of them are also spreading viruses and bacteria, therefore, the destruction of insect pests must be treated responsibly.
The main pests:
- Aphids - small insects of silver-green color. They feed on juice, while secreting sticky molasses. Sooty fungi begin to multiply on it. The presence of aphids is easy to detect - insects live in large colonies. Apply spraying with "Karbofos" or "Spark". You can also plant nearby plants that aphids cannot tolerate - carrots or tobacco.

- Cabbage fly - It is dangerous in that it lays larvae that infect the root system of the plant. As a result, the leaves become gray, and the bush begins to wither. Treat the crops with Thiophos at the end of May. From folk remedies, spraying crops with a decoction of tobacco helps.

- Cruciferous fleas - small black bugs feeding on the top of the leaf plate. It is difficult to notice them, but you can see small sores on the leaves. They appear in hot and dry weather. In order to prevent the pest from reaching the beds, often pour the cabbage in the heat.

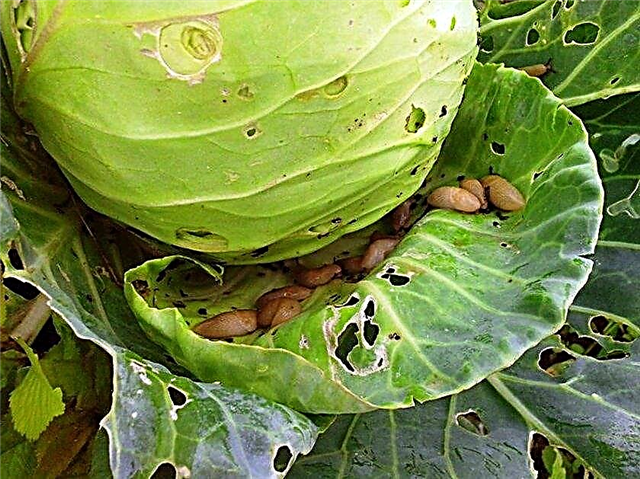
- Slug - big lovers of cabbage. To combat them, farmers sprinkle aisles with crushed shells or eggshells.

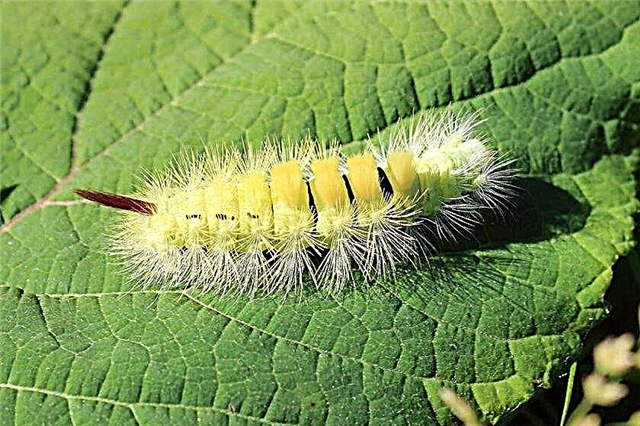
- Bright yellow furry caterpillar - This is the larva of a cabbage butterfly-whitish. She eats leaves. To protect cabbage, some farmers cover the net with crops at the end of May. This prevents butterflies from landing and laying eggs. If there are already caterpillars, then the treatment is applied by Fitoferm, Kinmiks or Kemifos.

Features of harvesting and storage of crops
The crop of this variety ripens 130–140 days after emergence. Cabbage is removed at an air temperature of at least + 5 ° C. Heads of cabbage are cut with a sharp knife, leaving a stalk 8–12 cm high. In the cellar, cabbage will be stored for up to 3 months at a temperature of 0 ... + 5 ° C, good ventilation and humidity of 90–95%. Storage methods are different: in drawers, boxes or on the grill, in the cells of which the stumps are inserted.
Important! Before you send cabbage for storage, it must be dried. For this, the crop is kept for 2 days outdoors, under a canopy, or in a well-ventilated area.
When cooking cabbage, consider some rules:
- eat raw or slightly processed cabbage - this is very useful;
- the preparation of cabbage at high temperatures destroys active enzymes, so the less it is subjected to heat treatment, the more it preserves the compounds that are responsible for the anti-cancer effect;
- cut cabbage into slices about 1 cm in size - this also helps to preserve the activity of enzymes;
- do not leave chopped cabbage for a long time on the table, it is better to put it in the refrigerator.
 If you follow the basic rules for growing cabbage, you can easily get an excellent harvest. SB-3 F1 cabbage is not only unpretentious in care, but also extremely useful. And this is an additional plus from its cultivation on a personal plot.
If you follow the basic rules for growing cabbage, you can easily get an excellent harvest. SB-3 F1 cabbage is not only unpretentious in care, but also extremely useful. And this is an additional plus from its cultivation on a personal plot.