Among the many varieties of potatoes, new, recently obtained varieties deserve special attention. Breeders improve their productivity, make them more resistant to disease. One of these varieties is Azhur, bred only 2 years ago. Read more about this variety and the features of its cultivation, read the review.
Selection history
Openwork was registered in the State Register of the Russian Federation in 2017. It is characterized by high taste properties and is recommended for cultivation in a temperate climate of central Russia and its central regions. This is the 4th winter hardiness zone with a minimum winter temperature of –35 ° C. The variety is also adapted to the climate and in regions with higher winter temperatures.
Given that young tubers can be eaten already on the 45th day, in the southern regions they practice planting Azhur 2 times a year: in early spring and summer, after harvesting. "Agricultural company Zedek." The aim of the selection was to obtain potatoes with high productivity.

Botanical Description
Potato - perennial. Its leaves die off after flowering and tuber formation. Flowers are pollinated by bumblebees and other insects. After flowering, small rounded green fruits form on the stems. In each of them - about 300 seeds.
New varieties of potatoes are obtained from seeds. Subsequently, the resulting variety propagates, like the rest, vegetatively by planting tubers or their fragments. For the formation of a bush, it is necessary that the fragment has 3-4 eyes. Bushes propagating from tubers are clones of the parent plant.
Important! Early varieties are eaten first. Their peel is thinner than in later ones, and this significantly affects the durability of tubers.
Tuber
The variety is distinguished by medium-sized, uniform tubers weighing from 100 to 120 g. One bush of Azhur will provide 10–13 identical potatoes. According to the results of tests that any variety passes before registration in the State Register, the yield was 187-410 kg / ha. Azhur showed maximum productivity in the Bryansk region. But mainly it depends on the climate, as well as on the fertility of the soil.

Tuber Characteristic:
- basic: homogeneous, about the same weight of 100-120 g;
- peel color: pink;
- pulp color: light cream;
- shape: oval;
- eyes: small.
Important! People diagnosed with diabetes need to control their blood sugar by eating potatoes. Its glycemic index — 95 GI, and it is almost 2 times higher than the norm for diabetics.
Kustov
The bush Azhura sprawling and vigorous, reaches a height of 55 cm. The leaves are large. The edge of the leaf plate is wavy, slightly jagged. The color is dark green. The flowers are purple. They can be formed not so much, but this does not affect the yield.
Grade characteristics
The variety is considered an early, high-yielding, table. Its homogeneous tubers have good taste characteristics, including starchiness at the level of 13–16%.

Disease immunity
The variety is not affected by cancer and scab, is moderately resistant to late blight. Most varieties are susceptible to rot if they are in too wet soil, so be careful when choosing a site - this will help reduce the risk of fungal diseases.
Ripening time
Openwork is an early ripe variety. You can dig up tubers already on the 45th day after the emergence of seedlings. It will take 70–75 days to fully mature.
Did you know? In 1995, potatoes traveled in space aboard the Columbia spacecraft. The vegetable was the first food that was grown in low Earth orbit.
Productivity
Productivity consists of 2 key quantities: the number of tubers per unit area and their weight. Both parameters depend on soil fertility. On average, 1 bush of Azhura is 10–13 medium-sized potatoes weighing about 100 g.
The yield of the variety shown in the studies is 187–410 kg / ha. This is a big variation, but it really shows the difference in the fertility of the plots. The originator declared productivity - 500 c / ha.
Keepiness
The storage temperature of the tubers is affected by the storage temperature, the presence of pathogens in the room where the crop and the health of the tubers are stored before being stored. The originator claims a 94% keeping quality, but this indicator may vary.

Rules for planting potatoes in open ground
Planting potatoes includes:
- preparation of seed material;
- presowing soil preparation;
- landing.
Optimal time for landing
Potato is a vegetable of cool weather, and it is planted a month before the date of the last freeze. Air temperature should not be lower than + 5 ° С. This temperature is set by the end of March. You can continue landing all April.
Did you know? Despite the fact that on our menu, potatoes have become an obligatory product, they began to consider it edible not so long ago. The first such step was taken by representatives of the medical faculty of the University of Paris in 1772.
Site selection and soil preparation
The soil should be well drained and not subject to waterlogging. Potatoes are loyal to soil types, but the best is well-drained loam. Avoid heavy clay soils. They do not allow air to pass through, flatten the potatoes and retain too much moisture during rains.
Sandstones lose moisture too quickly, so they are diluted with heavier soil to slow drying. The required acidity level is 5.5 to 7 pH. For acidic soils, it is recommended to add dolomite flour, lime or chalk for deoxidation in the fall.

You cannot add these substances simultaneously with fertilizers. For example, nitrogen and lime cancel each other out. On acidic soil, plants are weak, yields are low, and the incidence of decay is also increasing. Potatoes need at least 6 hours of sunshine per day. He will also need weekly watering.
If you cover the soil with mulch, this will help prevent excessive drying of the soil, provide the tubers with an optimal temperature for development. Root crops grow better at temperatures from + 15 ° C to + 21 ° C. Soil acidity level of 5.0–5.5 pH minimizes the risk of developing fungal diseases, including scab.
Good and bad predecessors
Mass cultivation of the same culture or related crops leads to an increase in the population of pests or pathogens. In addition, plants consume nutrients, depleting the soil. To solve these problems, crop rotation must be observed.

Fundamental rules:
- Divide the entire site into several areas (up to 4) for the crops you grow.
- Early potatoes can be planted after cucumber, pumpkin, cabbage, and legumes.
- Potatoes should not be grown after potatoes in the same area last season or after tomatoes, eggplant and pepper.
- You can return with planting potatoes to the same site no earlier than 5 years later.
- If the plot is too small, and potatoes can only be planted on it, then sow the plot with green fertilizers (green manure) after harvesting. It can be legumes, rye and other crops. They loosen the soil and fertilize it with nutrients.
It is important to consider that plants are divided into 4 main groups:
- Legumes (beans, peas, beans).
- Roots (radish, carrots, potatoes, onions, garlic, beets, rutabaga, sweet potato, shallots).
- Leafy greens (spinach, chard, cabbage, cauliflower, broccoli).
- Fruiting (tomatoes, sweetcorn, cucumbers, pumpkin, zucchini, eggplant).
Preparing planting material
Potatoes are planted with tubers or parts of tubers. A few weeks before planting, seed potatoes are placed in a warm room with a temperature of 15 ° C to + 21 ° C. When the emerged sprouts reach a size of 0.5 cm - the potato is almost ready for planting.

If planting will be carried out by fragments of tubers, then the incisions are performed with a sterile knife, then the material is dried for 2-3 days. Each fragment should have at least 2 eyes.
Technology, layout and depth of landing
Technically, landing involves three stages:
- Preparation of the site, which begins in the fall.
- Preplant planting of potatoes.
- The procedure itself.
There are several basic landing methods:
- Trench method. The depth of the trenches is 30 cm, the distance between them is 50–70 cm. The bottom of the trench is covered with straw to ensure the correct moisture regime. On top of the straw lay a layer of organic fertilizer - manure or compost. A layer of soil is laid above and ash is added. Lay the tubers at a distance of 30 cm from each other and close the trench with soil. The location of the trench is from north to south.
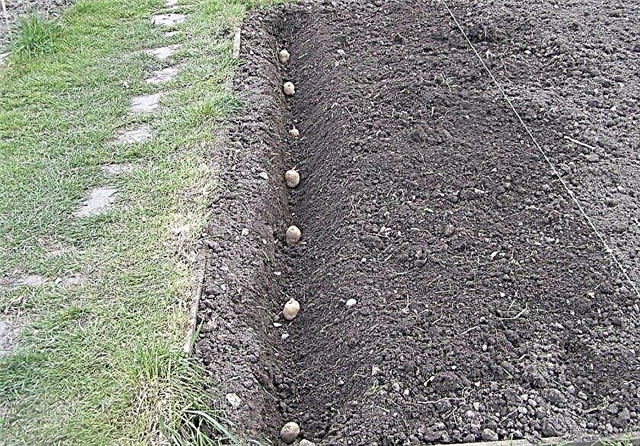

- Traditional for personal households is the “shovel” method. Wells are made on the plot with a distance between them of 30–40 cm. Depth is 10 cm. Rotten manure or compost is laid on the bottom of the hole, then a small layer of soil. Potatoes are laid on it and covered with soil.
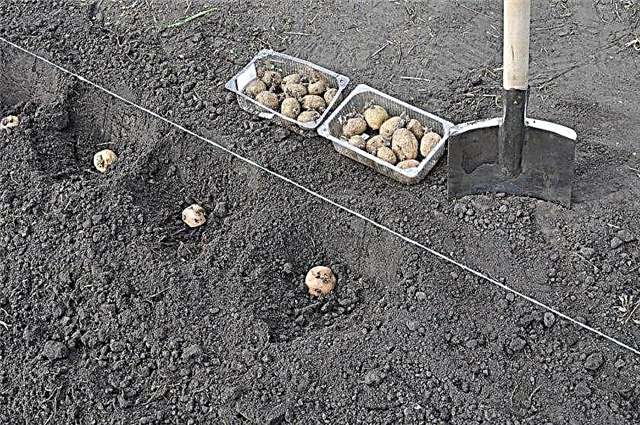

- Combs first from the soil with a distance between them - 70 cm. Potatoes are laid in them at a distance of 30–40 cm between tubers. As they grow, they grow up the potato and get a crest height of up to 40 cm.

Each method has advantages and disadvantages, but there is also a functional side - the trench method is good on light sandy soils, and the comb method - on clay ones. At the heart of any of them is the creation of the right conditions for tubers to grow and develop.
How to care for potatoes?
Crop care depends on the planting method. But any of them include:
- watering;
- hilling;
- fertilizer application;
- pest control.
Important! Potato tubers that have received excessive sun exposure turn green. It is a plant poison — solanine. It can lead not only to poisoning, but also to death. Green areas on potatoes must be cut off.
Irrigation mode
The frequency of watering depends on how quickly the soil loses moisture. Sandy soil is watered more often - 2 times a week. Improving the situation will help mulching. Coating materials, sawdust, straw or others, will prevent the quick drying of the soil and its compaction. The clay area is watered once a week.

Watering before flowering is needed in order to organize optimal conditions for the growing season. During flowering, tubers are laid and watering is also necessary. But when the bushes stop growing, and the stems begin to wilt, the irrigation is stopped.
Watering Rules:
- Do not water until the first hilling. This contributes to the wider development of the root system.
- Do not water deeper than 40 cm (there are no potatoes).
- Ensure uniform watering.
Did you know? In the XIX century, potatoes in Alaska became the only means that prevented scurvy from gold prospectors and could be stored for a long time. The price of tubers was so high that it equated to the cost of gold.
Top dressing
Immediately after germination, the aerial part of the plant begins to develop. At this stage, you need to intensively supply the plant with water and nutrients. Then the root system begins to form.
Essential Potato Substances:
- nitrogen - to stimulate growth, increase the number of leaves and enhance photosynthesis;
- phosphorus - to accelerate the growth of the root system;
- potassium - to stimulate the growth of roots and leaves, regulate water balance and metabolism.

The first top dressing is carried out 2 weeks after planting. To do this, choose a fertilizer with equal parts of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in it. The inorganic fertilizer application rate is 7 kg of fertilizer per 300 m² plot. Continue feeding every 4 weeks and stop 2 weeks before harvesting.
Weeding and loosening the soil
Removing weeds leaves more nutrients for the tubers and makes harvesting easier. Combating them is combined with soil loosening and hilling - an increase in the embankment around the potato. The purpose of hilling is to increase the volume of the root system and, accordingly, increase the number of tubers.

The procedure is carried out with any planting method, starting from the moment when the stems reach a height of 10-15 cm, that is, approximately 2 weeks after planting. The second hilling is carried out during flowering. It is believed that tuberization occurs at this very moment. But such a statement is not true for all varieties. After the potatoes have flowed out, the earthing up is not carried out.
Did you know? The heaviest potato in the world weighed 4.98 kg. This is enough to cook 70 servings of french fries in «Mcdonalds».
Preventive treatment for diseases and pests
Potato diseases appear as spots on leaves, plaque, foliage wilting. Viruses and bacteria enter the plant tissue due to mechanical damage or damage by pests.
The main diseases of potato:
- Bacterial wilt or brown rot - The most serious bacterial disease. It starts with yellowing leaves. Then they darken and dry, and white mucus appears on the stems. An effective counteracting agent is compliance with crop rotation rules.
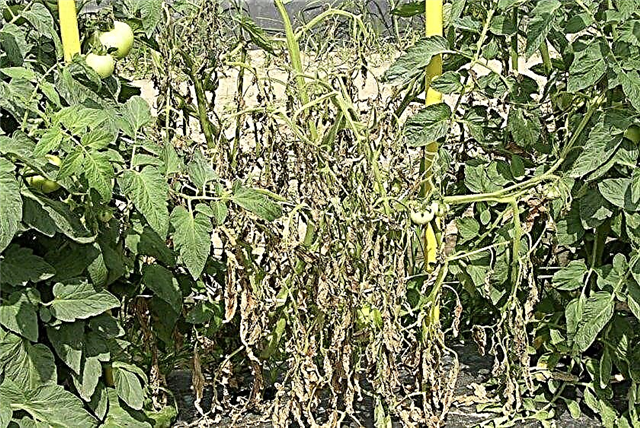

- Black leg of potato and soft rot of tubers spread in warm and humid weather. First of all, the lower part of the stem is affected, and then blackness and wilting move up. Humidity control and preventing waterlogging is the main way to prevent disease.
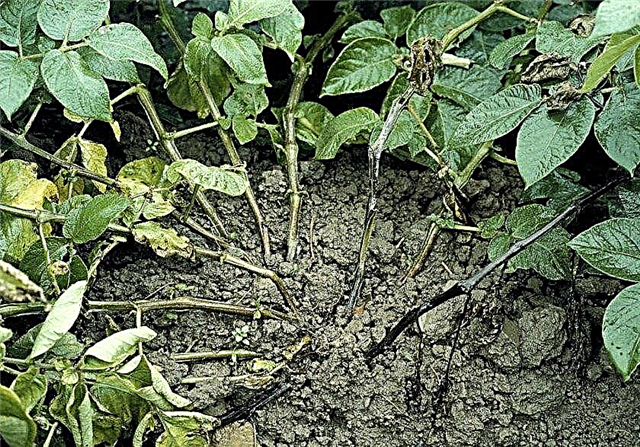

- Ring rot is a recurring disease problem in temperate climates. Symptoms usually appear mid-season or later, and include wilting of the stems. The plant becomes sluggish, brown rings are visible on sections of the stem. Prevention is the use of disease resistant varieties.
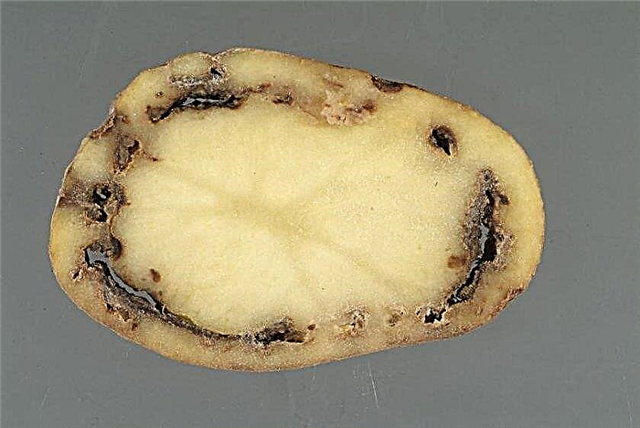
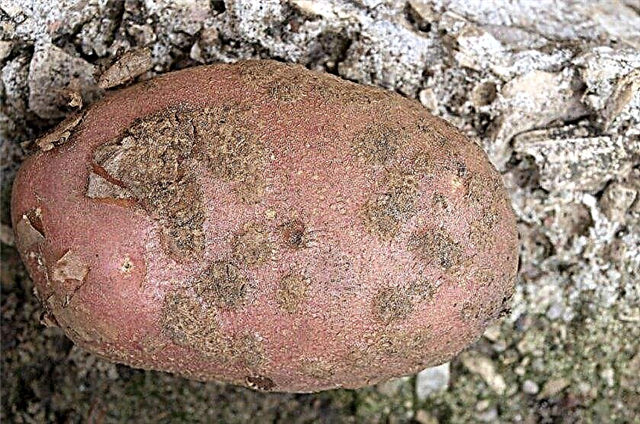
- Scab of potato there are several types. Its main signs are brown and hardened spots on tubers, covered with cracks. Prevention - planting disease-resistant varieties. Openwork also belongs to such.

- Late blight affects potato tops after flowering. It appears in the form of dark spots on the leaves. Affected stems quickly fade. When the first signs of the disease appear, they are sprayed with Ridomil and Fitosporin preparations.

- Leaf chlorosis or yellowing of leaf blades appear in the second half of summer and are not a disease, but rather symptoms of a lack of nutrients. As a treatment, spraying the bush with iron sulfate is used.

Like other plants, pests attack potato crops. Hilling is an effective method of controlling leaf pests, as this removes most of the leaf mass under the ground.
The main pests of potatoes:
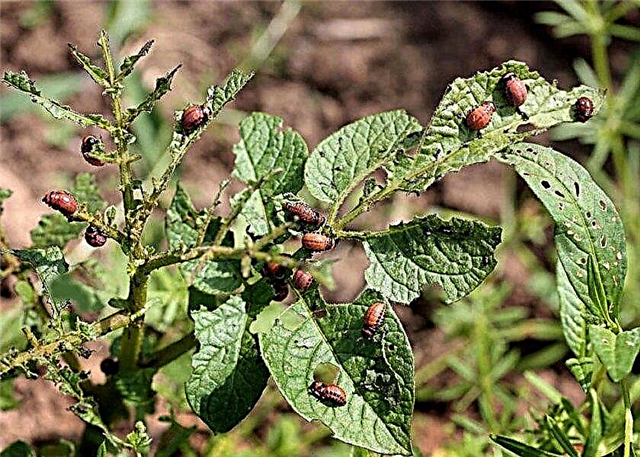
- Colorado beetle - The most common pest, feeds on leaves. The beetle is inedible for birds, therefore, in small areas of potato, beetles and their larvae are collected by hand, shaking in a special container. Of chemicals, it is recommended to use the preparations "Aktara" and "Prestige".

- Caterpillars - larvae of various butterflies, including potato scoops, leaf beetles. Larvae that damage tubers can also be dangerous. The Zolon preparation will help fight caterpillars.

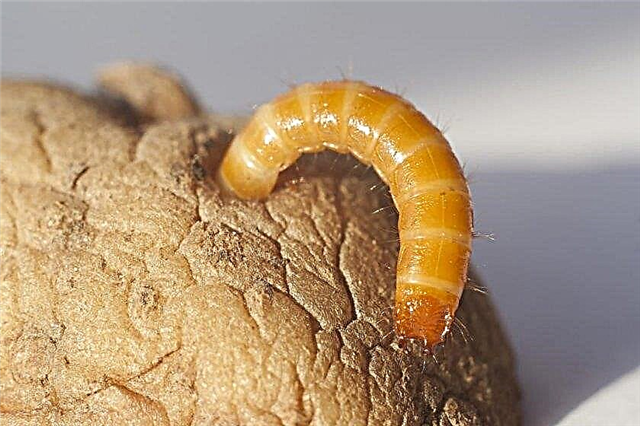
- Wireworms - larvae of the nutcracker, damage tubers. Among environmentally friendly, but effective ways to deal with them - planting mustard next to potatoes. Its essential oils are toxic to wireworms and cause the pest to leave the area.

- Nematodes - Microscopic worms that live in both tubers and leaves. To combat them, they use soil treatment with boiling water to a depth of at least 20 cm. Also, tubers and soil are treated with Karbofos.
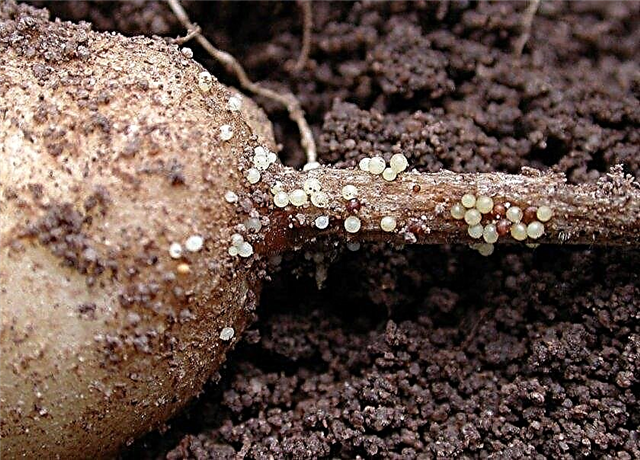

- Aphid less likely to affect potatoes than other crops. These green little insects feed on leaf juice. Their vital activity weakens plants, and the sticky coating that aphids leave leaves serves as a medium for the reproduction of sooty fungi. From the pest, crops are treated with a solution of insecticidal soap, and they are also attracted to the site of insect predators. So, one ladybug is able to eat about 5000 aphids in her life.

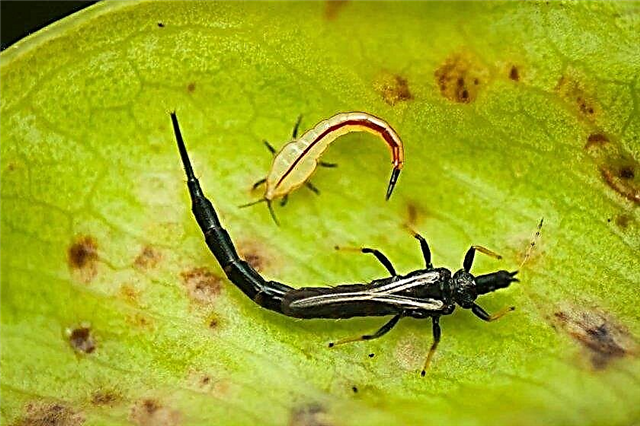
- Thrips - thin, elongated insects that feed on juice. Their populations increase when dry and warm weather sets in, so the best way to deal with them is to moisten potato crops.

Harvesting and storage
If the weather is sunny and the stalks of the potatoes wilted, you need to wait another 2 weeks until the peel gets stronger, and the potatoes are not ready for harvest. From the moment the tops begin to fade, watering is not carried out.
Potatoes can tolerate light frost, but it is better to start digging before the threat of freezing occurs. This is true for those who spend 2 planting potatoes: in early spring and summer, after the first harvest. The maturity of Azhur is 75 days, but young tubers can be digged after 45 days.
Did you know? The maximum number of potatoes that are harvested from one bush — 167 kg. The record was recorded in 1974 in the Guinness Book of Records.
Potato harvesting technology:
- To collect potatoes, you need a shovel. If you need to dig a couple of potatoes for dinner - start from the outside of the bush. Carefully lift it with a shovel and take those tubers that you need. Then lower the plant into place and pour plenty of water.
- Digging potatoes for winter storage, make sure that the peel is sufficiently strong. If the peel is easy to wash, leave the potatoes in the ground, let them get stronger.
- Try not to damage the roots when digging. Damaged tubers cannot be stored and deteriorate quickly.

After harvesting, the tubers are dried in a room with a temperature of +7 ... + 16 ° C for about two weeks. This allows the peel to condense and heal micro-scratches that appeared during digging. Store tubers in boxes. In a dry room at a temperature not exceeding + 10 ° C.
Important! Do not wash the potatoes before laying, this will shorten their shelf life. Do not leave the potatoes in the sun, green, they will become toxic and unfit for food.
If timely to carry out simple activities for the care of potatoes, then you will get a good harvest on any soil. Variety Azhur is unpretentious and easy to care for, so you can no doubt grow it on your site.



























