Hydrangea today can be found in many household plots. The plant has excellent decorativeness, especially during flowering. However, there are times when the leaves change color, and the culture itself stops growing and fades. It is important for gardeners to know why this is happening, as well as the causes and symptoms of malaise, and to be able to take measures in time so that the plant does not die at all.
Brown spots on the leaves
The main reason for the appearance of brown spots on the leaves of hydrangea is the lack of nutrients in the soil, as a result of which the metabolism is disturbed. This phenomenon is often observed in panicled hydrangea, when the plant grows for a long time in one area (more than 8 years) or the soil is not fed in sufficient quantities with microelements, especially iron. First, the leaf plates are covered in yellow, and the veins remain green - this is a characteristic sign of the disease, called chlorosis. Over time, yellowness seems to rust, turning from edges to the center into brown spots.
It is impossible to start the disease, since a lack of iron will lead to the fact that the shrub weakens, ceases to bloom, develop and eventually perishes. In addition, a weakened plant is much more susceptible to insect attacks, viral and fungal diseases. For treatment, spraying with drugs "Agricole", "Chelate" or "Ferovit" is used. It is also recommended to feed the soil with a solution of potassium nitrate (40 g of the substance is dissolved in 10 l of water). The procedure is carried out three times with an interval of 5-7 days. This is followed by top dressing with iron sulfate.
Important! After pruning a diseased plant, thoroughly wash and disinfect the instrument, since the infection remains on it for a long time and there is a risk of infecting other crops.
Another reason that causes brown spots on hydrangea bushes is the penetration of soil pathogens that persist in plant debris. They provoke a disease - tracheomycotic wilting. First, the infection hits the roots, and then it moves higher. As a result, the shrub begins to turn yellow, then grow brown and wilt. On adult cultures, leaf veins often brown. The treatment with Fitosporin helps to cure the plant.
Red spots on the leaves
The main cause of reddening hydrangea leaves is an excess of nitrogen in the soil.. Against this background, the plant develops a disease - rust, which can also be complicated by thickened plantings. The spots are pink at first, but then darken and acquire a rich red tint. Branches with signs of rust must be completely cut off, even if the damage is very slight. Sections need to be greased with garden var. After this, the shrub should be treated with fungicide. A good result is given by the solutions of the Skor and Chorus preparations.
Heavy watering in wet weather can trigger the development of fungal spores, resulting in septoria. The infection progresses rapidly: first it affects the lower shoots, and then spreads to the upper ones. The leaves in this case acquire a red or red-brown color. The bush dries quickly, drops leaves. As in all previous cases, it is necessary to remove the affected parts of the shrub and spray with “Profit”.
Black spots on the leaves
Sometimes black spots can be seen on hydrangea leaves. As in most cases, the reason for their appearance is a violation of the rules of agricultural cultivation. In particular, if a plant grows for a long time in waterlogged soil, its root system is gradually destroyed, and immunity weakens. As a result, wet black spots appear on the leaves. If they have not yet covered the entire plant, you can try to cure it.
It is best to do a transplant by doing the following:
- Prepare the landing pit in a suitable place, lay the drainage layer on the bottom.
- Dig a sick bush, shake the ground from the rhizome.
- Cut off all damaged areas, spray the plant with a solution of potassium permanganate.
- Transplant it to a new place, and then carry out the processing of the Bordeaux mixture.
Did you know? Hydrangea grew on Earth more than 70 thousand years ago. The remains of the plant were found in North America and China.
Another reason for the appearance of black spots is sunburn, resulting from the long stay of the bush under the sun. In this case, the spots are dry. If you do not take any measures, the spots will spread throughout the bush, the leaves will begin to fade and crumble. As in the previous case, transplantation to another section located in partial shade will help to save the situation. It is important to fertilize and acidify the soil so that the plant takes root well and regains its strength.
Other common diseases
Scientists have found quite a few diseases that can ruin hydrangea. Most of them are not associated with improper care, but are transferred from diseased cultures. Almost all of them are treated in the early stages, so it is important to establish the symptoms in time and start treatment so as not to lose the ornamental shrub.
Fungal
The categories of fungal diseases that can kill hydrangea include the following:
- Powdery mildew - characterized by the appearance of small yellow spots and a whitish coating on the sheet plates, which at first is easily erased by fingers. Over time, purple formations can be seen on the lower plates. There can be many reasons for the defeat: spores are easily tolerated by wind, insects, groundwater. If you find that this disease has affected the culture, you must immediately begin treatment, otherwise it will die.
 First you need to cut off all the painful fragments and burn, so that the fungus does not spread to other plants on the site. It is further recommended to spray the shrub with a powerful fungicide. In the fight against fungal diseases, Fitosporin showed itself well, from which a solution is prepared (5 g of the product per 10 l of water).
First you need to cut off all the painful fragments and burn, so that the fungus does not spread to other plants on the site. It is further recommended to spray the shrub with a powerful fungicide. In the fight against fungal diseases, Fitosporin showed itself well, from which a solution is prepared (5 g of the product per 10 l of water).Important! The main active ingredient of the Fitosporin preparation is the bacterium of hay bacillus. She quickly dies in the sun, so the treatment must be carried out in the evening or in cloudy weather.
- Gray rot. Fungal disease actively develops in a moist, dense environment, affecting the soft tissues of the plant. A soft ashy coating, uneven holes are clearly visible on the leaves. At the peak of the disease, leaf platinum begins to crumble into dust. Starting treatment, it is necessary to remove dead tissue, treat the bush first with a weak solution of potassium permanganate, and then with Fundazol. If the disease has gone too far, it is better to dig and burn the plant.
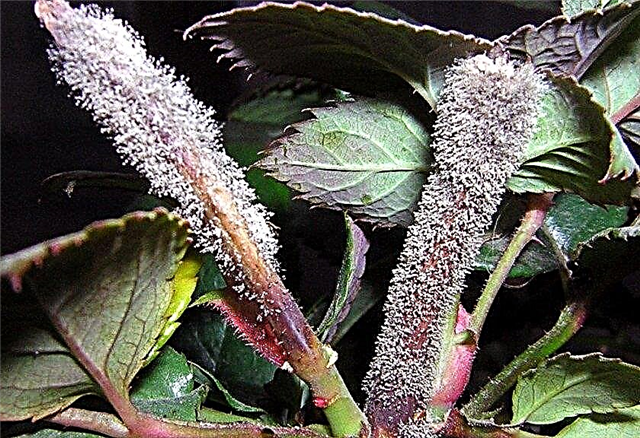

- White rot. The disease develops rapidly in closed greenhouses and greenhouses. In open garden areas is rare. The reasons may be infection from neighboring crops, the penetration of fungal spores from plant debris. The disease affects the hydrangea root, depriving the shoots of nutrients. The stems begin to rot at the base, and a white coating appears on the leaves, similar to cotton wool, which is later covered with dark spots. Affected fragments must be removed, and the bush treated with a solution of copper sulfate.

- Peronosporosis. Another name for this disease is downy mildew. It occurs under special climatic conditions when there is a high level of humidity in hot air. Symptoms are darkening oily spots on leaf blades that later shift to shoots. The plant can be cured only at the initial stage. The diseased areas are cut out, the sections are treated with potassium permanganate, and the shrub itself is sprayed with the Optimo or Kuproksat preparations.
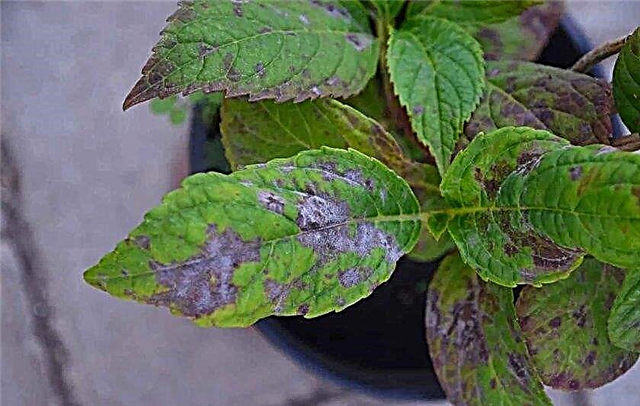

Viral
In addition to fungal diseases, hydrangeas in the garden are also threatened by viral ailments. There are only two of them, but the danger lies in the fact that the disease is practically untreatable.
Did you know? Slug eggs can hibernate and persist 3-4 years, and then the cubs hatch under favorable conditions.
These include:
- Ring spotting. The disease is determined by the appearance of necrotic spots on the leaves. Leaf plates begin to wrinkle, after which the plant dies. It will not be possible to cure the bush, because there are still no drugs that can suppress this virus. The sick bush needs to be dug up and surely burned.
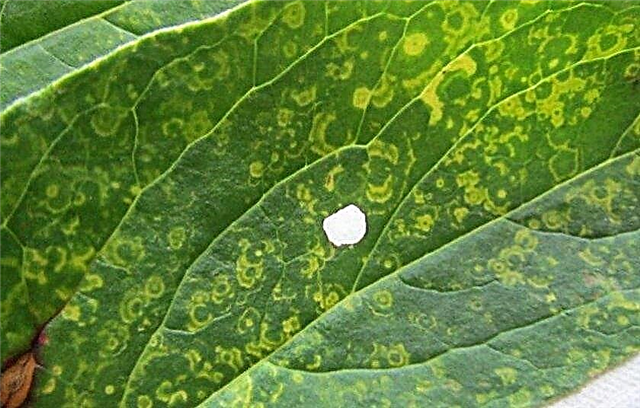

- Crayfish. No less dangerous ailment, the causes of which have not yet been established. The main symptom is the appearance on the leaves and stems of brown, as if rusted spots. On the back of the leaf plates, you can see small sores. If symptoms have just begun to appear on the shrub, you can try to prune and process potassium permanganate. However, the chances of recovery are very few. It’s better to get rid of the plant right away.
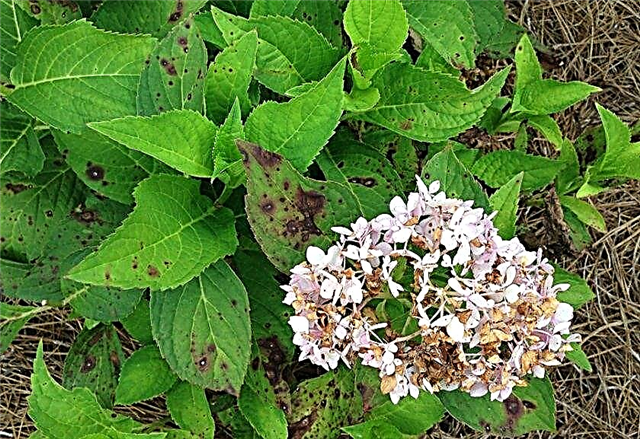

Pests and how to deal with them
Various diseases, including viral and fungal ailments, bring great harm to hydrangeas. However, at least, these phenomena can be prevented, unlike attacks by insect pests.
The most dangerous enemies of hydrangea are:
- Gall nematode - a round worm that affects the root system of the plant, on which yellow-brown swellings form. The shrub looks oppressed, stops growing, and the leaves become stained and curled. You can overcome the pest with the help of drugs "Phosphamide" or "Mercaptophos".
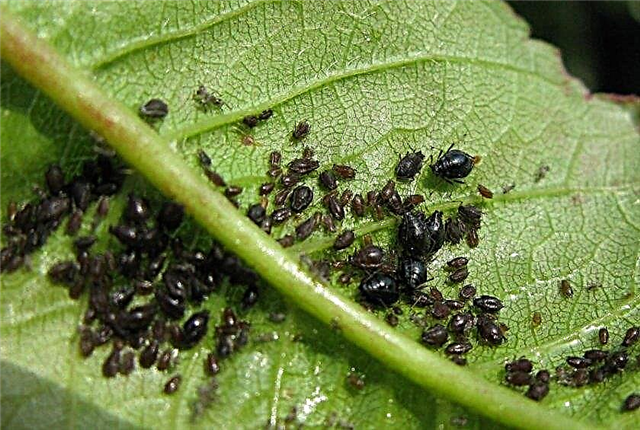
- Leaf aphid - a sucking insect that can completely destroy a plant if its colonies are not eliminated on time (visible on leaf blades in the form of black-brown spots). As a prevention of the appearance of aphids, you need to regularly clean the area from fallen leaves and weeds - this is where the insect lays eggs. You can deal with the pest using such a solution: 300 g of ash and 100 g of grated laundry soap are dissolved in 10 liters of water, filtered. All shoots and leaves are treated with this mixture. If this method does not help, you can spray with a chemical preparation, for example, Acarin.

- Spider mite - a small insect that actively equips its settlements during dry weather. Gardeners need to take this into account and carry out periodic evening sprayings of plants under such weather conditions. The presence of the spider mite can be determined by the appearance of a thin web and black spots on the foliage (colonies). First of all, it is necessary to remove all damaged areas, after which it is imperative to spray the Akarin culture.

- Garden slug - This pest progresses most often where there is shadow and moisture. It often hibernates with hydrangea under general shelter, so it can be seen on bushes in early spring. One can also find slugs in the summer, as they move around the site, looking for secluded wet corners of the garden. The pest literally eats the plant, starting with leaves that quickly fade, and ending with shoots. In order to prevent hydrangea from invading slugs, it is recommended to install containers with insecticides around shrubs (for example, Aktara). If you notice the presence of pests on the bush, they can be removed manually. After this, it is recommended to treat the plant with Molluscocide.

Lushly blooming hydrangea is the pride of any gardener, however its cultivation requires a lot of attention and effort. It is very important to choose the most suitable site for planting, water and feed the crop on time. Also, preventive treatment with drugs that exclude the development of diseases and pest attacks cannot be overlooked.

 First you need to cut off all the painful fragments and burn, so that the fungus does not spread to other plants on the site. It is further recommended to spray the shrub with a powerful fungicide. In the fight against fungal diseases, Fitosporin showed itself well, from which a solution is prepared (5 g of the product per 10 l of water).
First you need to cut off all the painful fragments and burn, so that the fungus does not spread to other plants on the site. It is further recommended to spray the shrub with a powerful fungicide. In the fight against fungal diseases, Fitosporin showed itself well, from which a solution is prepared (5 g of the product per 10 l of water).



















